Biology Pathways
Biology Unit 1


Overview
How do organisms regulate their functions?
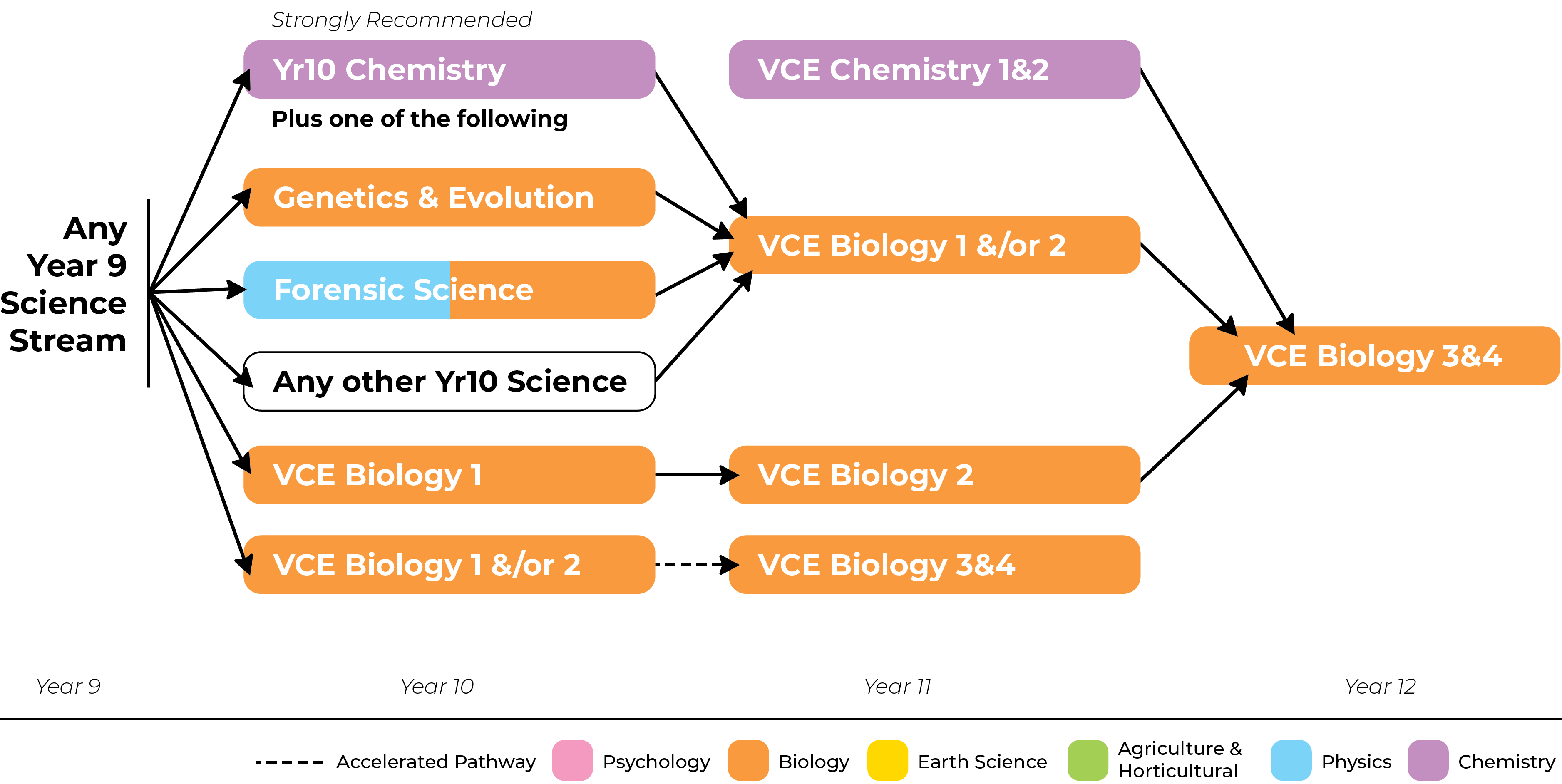
In this unit you will examine the cell as the structural and functional unit of life, from single celled to the multicellular organisms, including the requirements for sustaining cellular processes.
You will focus on cell growth, replacement and death and the role of stem cells in differentiation, specialisation and renewal of cells. You explore how systems function through cell specialisation in vascular plants and animals, and consider the role homeostatic mechanisms play in maintaining an animal’s internal environment.
Download > VCE Biology Study Design
Prerequisites
Year 10 Chemistry + Year 10 Forensics or Genetics and Evolution are recommended
Areas of Study
- How do cells function?
- How do plant and animal systems function?
- How do scientific investigations develop understanding of how organisms regulate their functions?
In the first area of study, you will explain and compare cellular structure and function and analyse the cell cycle and cell growth, death and differentiation.
In the second area of study, you will explain and compare how cells are specialised and organised in plants and animals, and analyse how specific systems in plants and animals are regulated.
Unit Assessment
Assessment for Outcomes 1 and 2 may include: a case study analysis, a bioinformatics exercise, a data analysis, reflective annotations of a logbook of fieldwork activities, media analysis, simulation activities, response to an issue, a scientific poster, a practical report.
Outcome three will be assessed by a report of a student-adapted or student-designed scientific investigation using a selected format such as a scientific poster, an article for a scientific publication, a practical report, an oral presentation, a multimedia presentation or a visual representation.
Pathways
Biology Units 1 and 2 will typically be studied in Year 11. Students undertaking acceleration may do these units in Year 10.
It is recommended that both Units 1 and 2 be taken before attempting Units 3 and 4 but students with strong results in Unit 2 who are prepared to catch-up on the relevant Unit 1 content in their own time will still be accepted into the Unit 3 and 4 course.
Biology Unit 2

Overview
How does inheritance impact on diversity?
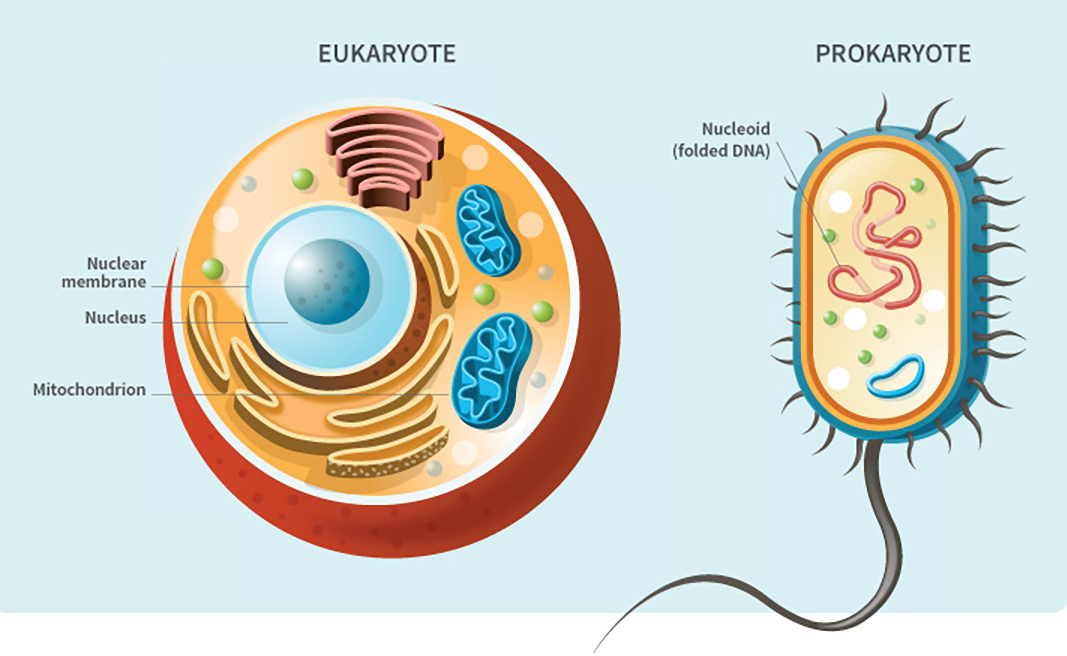
You will explore reproduction and the transmission of biological information from generation to generation and the impact this has on species diversity. You will apply your understanding of chromosomes to explain the process of meiosis.
You will consider how the relationship between genes, and the environment and epigenetic factors influence phenotypic expression. You will explain the inheritance of characteristics, analyse patterns of inheritance, interpret pedigree charts and predict outcomes of genetic crosses.
You will analyse the advantages and disadvantages of asexual and sexual reproductive strategies, including the use of reproductive cloning technologies. You will study structural, physiological and behavioural adaptations that enhance an organism’s survival. You will explore interdependences between species, focusing on how keystone species and top predators structure and maintain the distribution, density and size of a population. You will also consider the contributions of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander knowledge and perspectives in understanding the survival of organisms in Australian ecosystems
Download > VCE Biology Study Design
Prerequisites
Unit 1 Biology Recommended
Areas of Study
- How is inheritance explained?
- How do inherited adaptations impact on diversity?
- How do humans use science to explore and communicate contemporary bioethical issues?
Unit Assessment
Assessment for Outcomes 1 and 2 may include: a case study analysis, a bioinformatics exercise, a data analysis, reflective annotations of a logbook of fieldwork activities, media analysis, simulation activities, response to an issue, a scientific poster, a practical report.
Outcome 3 will be assessed by a response to an investigation into a bioethical issue relating to genetics or reproductive science or adaptations beneficial to survival
Pathways
Biology Units 1 and 2 will typically be studied in Year 11. Students undertaking acceleration may do these units in Year 10.
It is recommended that both Units 1 and 2 be taken before attempting Units 3 and 4 but students with strong results in Unit 2 who are prepared to catch-up on the relevant Unit 1 content in their own time will still be accepted into the Unit 3 and 4 course.
Biology Unit 3

Overview
How do cells maintain life?
In this unit you will investigate the workings of the cell from several perspectives. You will explore the relationship between nucleic acids and proteins as key molecules in cellular processes. You will analyse the structure and function of nucleic acids as information molecules, gene structure and expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and proteins as a diverse group of functional molecules. You will examine the biological consequences of manipulating the DNA molecule and applying biotechnologies.
You will explore the structure, regulation and rate of biochemical pathways, with reference to photosynthesis and cellular respiration. You will explore how the application of biotechnologies to biochemical pathways could lead to improvements in agricultural practices.
You will apply your knowledge of cellular processes through investigation of a selected case study, data analysis and/or a bioethical issue. Examples of investigation topics include, but are not limited to: discovery and development of the model of the structure of DNA; proteomic research applications; transgenic organism use in agriculture; use, research and regulation of gene technologies, including CRISPR-Cas9; outcomes and unexpected consequences of the use of enzyme inhibitors such as pesticides and drugs; research into increasing efficiency of photosynthesis or cellular respiration or impact of poisons on the cellular respiration pathway.
Download > VCE Biology Study Design
Prerequisites
- Unit 2 Biology
- Year 10 Chemistry are advisable but not required by VCAA
Areas of Study
- What is the role of nucleic acids and proteins in maintaining life?
- How are biological pathways regulated?
Unit Assessment
- Unit 3 School assessed coursework (SAC’s) 20%
- Unit 4 School assessed coursework (SAC’s) 30%
- Unit 3 & 4 examination 50%
Outcome one will be an analysis and evaluation of a contemporary bioethical issue. Outcome two will be a comparison and evaluation of biological concepts, methodologies and methods, and findings from three student practical activities.
Pathways
Biology Units 1 and 2 will typically be studied in Year 11. Students undertaking acceleration may do these units in Year 10.
It is recommended that both Units 1 and 2 be taken before attempting Units 3 and 4 but students with strong results in Unit 2 who are prepared to catch-up on the relevant Unit 1 content in their own time will still be accepted into the Unit 3 and 4 course.
Biology Unit 4
Overview
How does life change and respond to the challenges?
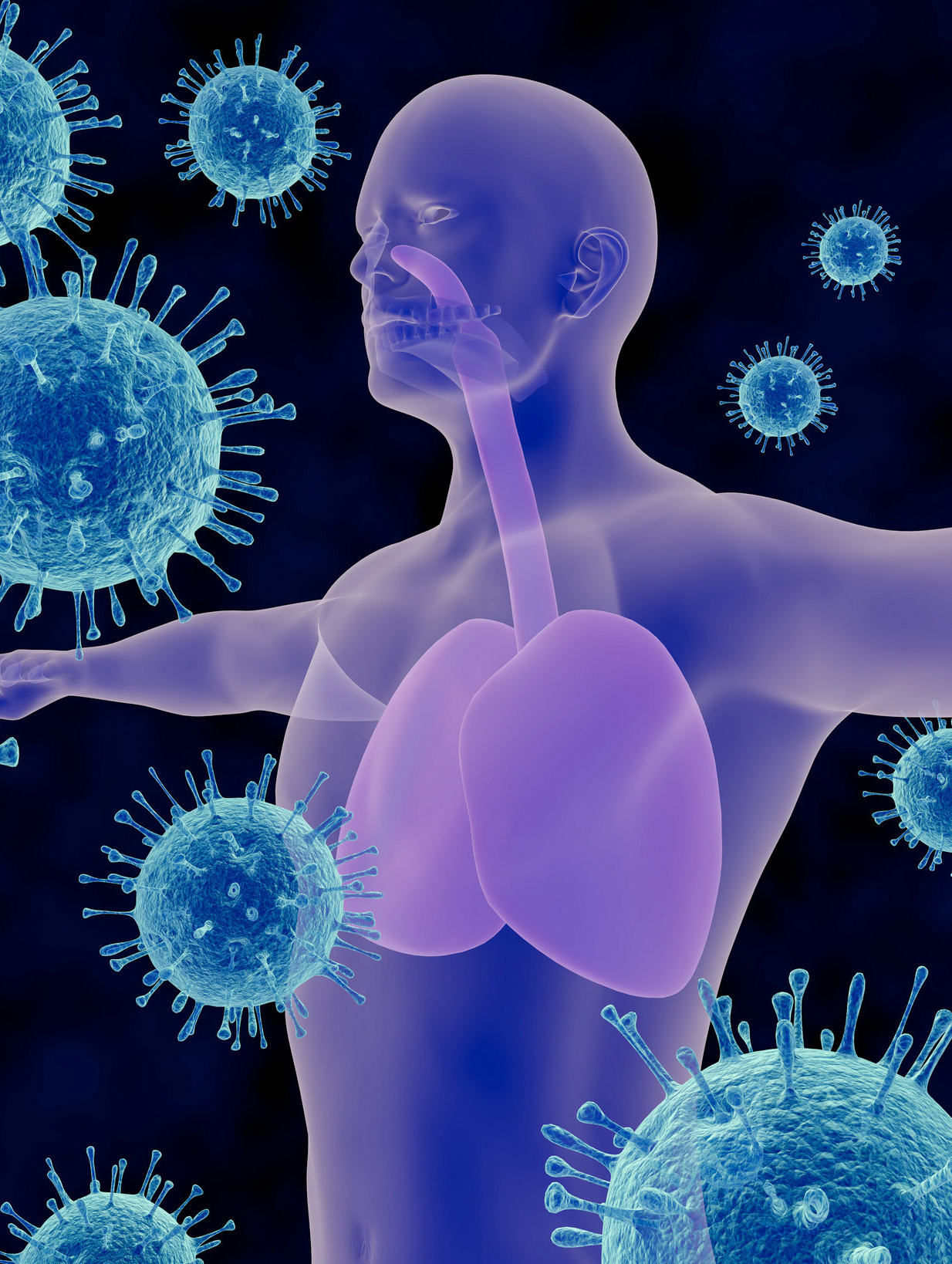
In this unit you will consider the continual change and challenges to which life on Earth has been, and continues to be, subjected to. You will study the human immune system and the interactions between its components to provide immunity to a specific pathogen. You will consider how the application of biological knowledge can be used to respond to bioethical issues and challenges related to disease.
You will consider how evolutionary biology is based on the accumulation of evidence over time. You will investigate the impact of various change events on a population’s gene pool and the biological consequences of changes in allele frequencies. You will examine the evidence for relatedness between species and change in life forms over time using evidence from paleontology, structural morphology, molecular homology and comparative genomics. You will examine the evidence for structural trends in the human fossil record, recognising that interpretations can be contested, refined or replaced when challenged by new evidence.
You will demonstrate and apply your knowledge of how life changes and responds to challenges through investigation of a selected case study, data analysis and/or bioethical issue. Examples of investigation topics include, but are not limited to: deviant cell behaviour and links to disease; autoimmune diseases; allergic reactions; development of immunotherapy strategies; use and application of bacteriophage therapy; prevention and eradication of disease; vaccinations; bioprospecting for new medical treatments; trends, patterns and evidence for evolutionary relationships; population and species changes over time in non-animal communities such as forests and microbiota; monitoring of gene pools for conservation planning; role of selective breeding programs in conservation of endangered species; or impact of new technologies on the study of evolutionary biology.
Download > VCE Biology Study Design
Prerequisites
-
Unit 3 Biology is required
Areas of Study
- How do organisms respond to pathogens?
- How are species related over time?
- How is scientific enquiry used to investigate cellular processes and/or biological change?
Unit Assessment
- Unit 3 School assessed coursework (SAC’s) 20%
- Unit 4 School assessed coursework (SAC’s) 30%
- Unit 3 & 4 examination 50%
Assessment tasks for Outcome 1 may be in the form of a test or analysis document. Outcome 2 is based on gene investigation techniques using the facilities at a tertiary laboratory. Outcome three will be the communication of the design, analysis and findings of a student-designed and student-conducted scientific investigation through a structured scientific poster and logbook entries.
Pathways
Biology Units 1 and 2 will typically be studied in Year 11. Students undertaking acceleration may do these units in Year 10.
It is recommended that both Units 1 and 2 be taken before attempting Units 3 and 4 but students with strong results in Unit 2 who are prepared to catch-up on the relevant Unit 1 content in their own time will still be accepted into the Unit 3 and 4 course.

